---
title: "Five Features of the Tiger CLI You Aren't Using (But Should)"
published: 2025-12-10T11:37:07.000-05:00
updated: 2025-12-10T11:38:39.000-05:00
excerpt: "Tiger CLI + MCP server: Let AI manage databases, fork instantly, search Postgres docs, and run queries—all from your coding assistant without context switching."
tags: AI, AI agents, PostgreSQL
authors: Jacky Liang
---
Last month, we launched [Agentic Postgres](https://www.tigerdata.com/blog/postgres-for-agents), the first Postgres database designed for AI agents. It includes an MCP server that gives agents direct access to your databases, instant zero-copy forks, Postgres and TimescaleDB documentation search, and more.
Alongside Agentic Postgres, we shipped a brand new CLI: [Tiger CLI](https://github.com/timescale/tiger-cli). It's how you manage your Tiger Cloud databases from your favorite terminal.
The basics work like you'd expect:
```shell
# Install Tiger CLI
curl -fsSL https://cli.tigerdata.com | sh
# Authenticate
tiger auth login
# Create a new database service
tiger service create --name my-database
# Connect to your database
tiger db connect
# Get your connection string
tiger db connection-string
# List all your services
tiger service list
```
These commands cover most day-to-day workflows. But Tiger CLI has a few features that makes the agentic development workflow significantly more intuitive, and you're probably not using them yet!
Here are five new features we launched that you aren’t using, but should:
1. **Let your AI manage your databases**: Install an MCP server that gives your AI assistant direct access to create services, run queries, and check connections
2. **Turn your AI into a Postgres expert**: Skills teach your AI Postgres best practices automatically, as if it’s been writing production-grade PostgreSQL for a decade+.
3. **Fork any database in seconds**: Create zero-copy clones of your database for testing migrations or spinning up staging environments
4. **Search Postgres docs from your editor**: Your AI can search PostgreSQL (across all versions) and TimescaleDB documentation without leaving your IDE or CLI
5. **Run SQL queries through your AI**: Execute queries against your database directly from your AI assistant
Let's look at each one.
## Let Your AI Manage Your Databases
As anyone coding with Cursor or Claude Code knows, nothing breaks flow more than having to leave your AI agent to execute CLI commands. Every time you need to check a database connection string, list your available services, or create a new database, you need to switch context. From your terminal, to the browser, back to your IDE, it’s easy to break out of your flow state.
The Tiger CLI now includes a [Model Context Protocol](https://modelcontextprotocol.io/docs/getting-started/intro) (MCP) server. If you're using an AI coding assistant like Claude Code, Cursor, or VS Code with Copilot, you can give it direct access to your Tiger Cloud databases.
This means your AI assistant can list your services, run SQL queries, create new databases, and check connection details, all without you switching to your terminal.
### Quick Setup
Install the MCP server for your assistant:
```shell
# Interactive (prompts you to pick your client)
tiger mcp install
# Or specify directly
tiger mcp install claude-code
tiger mcp install cursor
tiger mcp install vscode
```
We made it super easy to install the Tiger CLI in all of your favorite coding assistants\* through an interactive prompt that guides you through the installation.

Restart your AI assistant after installation.
\* We are constantly adding interactive installations for new coding assistants!
### Adding to Cursor via UI
If you prefer to configure Cursor (or other IDEs) manually instead of using `tiger mcp install`:
1. Open Cursor Settings
2. Look for “Tools & MCP” on the left sidebar
3. Click "Add MCP server"
4. Enter the following configuration:
- **Name:** `tiger`
- **Command:** `tiger`
- **Arguments:** `mcp`, `start`

5. Click "Save" and restart Cursor
Once configured, you'll see the Tiger MCP server listed in your MCP servers. The green indicator shows it's connected and ready.

### What You Can Do
Once installed, your AI assistant has access to tools like:
- `service_list` — List all your database services
- `service_get` — Get details about a specific service
- `service_create` — Create a new database
- `db_execute_query` — Run SQL queries against any service
For a full list of tools available to you and your agent, they are available in the [Tiger CLI README](https://github.com/timescale/tiger-cli?tab=readme-ov-file#available-mcp-tools) on Github.
For example, you can ask your AI assistant: "Show me all my Tiger Cloud services" or "Run `SELECT count(*) FROM events` on my production database."
The MCP server uses your existing CLI authentication, so there's no extra setup after `tiger auth login`.
## Turn Your AI Into a Postgres Expert
A new pattern of working with SQL has emerged as agentic coding has exploded in popularity.
You can now simply just tell an LLM what you want to do with your database, and it will write the SQL for you. You basically don’t even need to spend sweat, tears, or even fear (like you accidentally dropping a table, although this is still [completely within the realm of possibility](https://fortune.com/2025/07/23/ai-coding-tool-replit-wiped-database-called-it-a-catastrophic-failure/) when working with an agent) to learn how to write SQL.
But this AI-generated SQL actually has spawned a new problem, which is, AI-generated SQL works… until it doesn’t.
Your schema may pass tests, your queries may run… but six months later, as your application scales to millions of users, everything slows to a crawl.
The problem here is that LLMs are actually trained on millions of lines of SQL, absorbed from a billion blog posts (of differing quality), so while they “know” SQL, they don’t actually know what patterns actually scale. There are also hundreds of different dialects of SQL, with dozens of versions each.
It’s no wonder AI agents may not write the best SQL.
We’ve personally seen many common AI-generated mistakes, including:
- Using `VARCHAR(255)` instead of `TEXT` (the length limit doesn't help performance in Postgres)
- Using `SERIAL` instead of `BIGINT GENERATED ALWAYS AS IDENTITY`
- Missing indexes on foreign key columns (Postgres doesn't create these automatically)
- Using `TIMESTAMP` instead of `TIMESTAMPTZ` (timezone handling is painful to fix later)
These will not raise syntax or linter errors. Your tests will still pass. But trying to fix these mistakes later once your app is handling millions of users, means painful migrations, downtime, and explaining to your CEO why the database needs to go down for all your users to undergo maintenance. Sound familiar?
The Tiger MCP server ships with a variation of [Skills](https://www.tigerdata.com/blog/free-postgres-mcp-prompt-templates) (a [standard](https://www.claude.com/blog/skills) built by Anthropic) written by our most senior and experienced Postgres engineers. When your AI needs to design a schema, the MCP server automatically pulls the right “lessons” and then applies 30 years of Postgres best practices to your database design.
### Available Skills
The MCP server includes skills for common Postgres and TimescaleDB tasks.
- `design-postgres-tables`: Schema design with proper types, constraints, and indexes
- `setup-timescaledb-hypertables`: Hypertable configuration, compression, retention policies
- `migrate-postgres-tables-to-hypertables`: Converting existing tables to hypertables
- `find-hypertable-candidates`: Identifying which tables should become hypertables
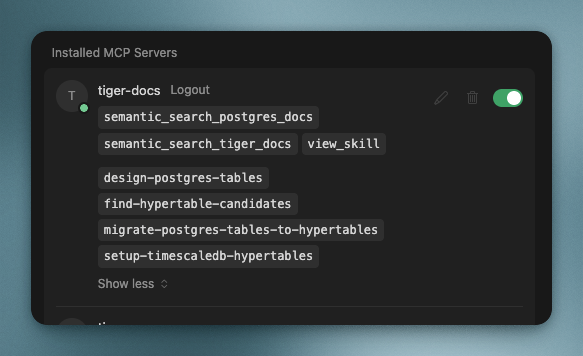
Your AI discovers and uses these automatically based on what you ask it to do. You don’t need to call them explicitly!
_We are continually adding new Skills. **Want to request new ones or contribute with your own?** Feel free to_ [_create an issue_](https://github.com/timescale/pg-aiguide/issues) _in our Skills Github repo._
## Fork Any Database in Seconds
Testing database migrations against production data is risky, but testing against fake data is also risky because you may miss edge cases. You need a real copy of your database but without the cost or time of duplicating everything manually.
Tiger CLI lets you create instant, zero-copy forks of any database:
```shell
tiger service fork --name my-staging-db
```
The fork created is a point-in-time copy that shares underlying data blocks with the original. You only pay for blocks that change. This makes forks lightweight enough to spin up for a single test and throw away when you’re done.
Database forking is especially useful when working in an agentic context, where if you are using multiple agents at once, you can fork multiple databases for different agents to work on without affecting the original database. Neat!
### Example Workflow
```shell
# List your services to find the source ID
tiger service list
# Fork your production database
tiger service fork --source-id svc_abc123 --name testing-migrations
# Connect to the fork
tiger db connect --service-id
# Run your migration, test it, then delete the fork when done
tiger service delete
```
## Search Postgres Docs From Your Editor
Postgres has been around for [almost 30 years](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PostgreSQL).
The documentation is incredibly extensive, spanning 18 versions and countless individual releases. A function that exists in Postgres 18 might not exist in 15. Syntax that worked in 14 now has better alternatives in 18.
Most AI-powered documentation search tools don’t account for these idiosyncrasies.
If not using docs search tools, and simply relying on an LLM’s own training data, well, they have training cutoffs, generally at least lagging by 6 months, so LLMs often suggest older methods that aren’t the most performant, or reference features that don’t exist in your version. This is actually a major problem with LLMs writing React and NextJS I’ve personally experienced in my side projects!
The Tiger MCP server includes search over PostgreSQL documentation from versions 14 to 18 and TimescaleDB docs for time series workloads. Your AI assistant can search version-specific docs without leaving your coding agent.
Your assistant gets access to:
- `semantic_search_postgres_docs`: Search PostgreSQL documentation (versions 14-18)
- `semantic_search_tiger_docs`: Search Tiger Cloud and TimescaleDB documentation

### No More Context Switching
Instead of leaving your editor to search docs, you can ask your AI assistant directly:
- "How do I set up continuous aggregates in TimescaleDB?"
- "What's the syntax for PostgreSQL window functions?"
- "Show me how to configure compression policies"
The assistant searches the actual docs and gives you accurate, up-to-date answers. You don’t even need to ask the agent to explicitly use the documentation search feature, it will just work.
P.S. This feature is enabled by default. If you ever need to disable it:
```shell
tiger config set docs_mcp false
```
## Run SQL Queries Through Your AI
You’re debugging an issue, you need to check row count, inspect a table’s schema, or run a quick query. You’re used to having to open a new terminal, find and remember the connection string, connect via psql, run the query, copy the results back (often jankily when done inside the CLI due to text wrapping). All these steps just for getting ONE number.
No more.
Once you’ve set up the MCP in your coding agent, your AI assistant can execute SQL queries (using the `db_execute_query` tool) directly against your databases.
This means you can stay in your editor and ask your AI:
- "How many events came in during the last 24 hours?”
- "Show me the 10 most recent orders"
- "What's the schema of the users table?"
### Example
Your AI writes the (performant) SQL, runs it, and returns the results. No more terminal switching, copy-pasting connection strings, remembering your environment, exact syntax for your `information_schema`.
## Get Started Now
Install the Tiger CLI and MCP server:
```shell
curl -fsSL https://cli.tigerdata.com | sh
tiger auth login
tiger mcp install
```
Then select your AI assistant (Claude Code, Cursor, VS Code, Windsurf) and you're ready to go.
Don't have a Tiger Cloud account? [Sign up for free](https://console.cloud.timescale.com/signup) — no credit card required. Create your first database, then try out these CLI features.
## Resources
1. [Postgres for Agents](https://www.tigerdata.com/blog/postgres-for-agents)
2. [How to Train Your Agent to Be a Postgres Expert](https://www.tigerdata.com/blog/free-postgres-mcp-prompt-templates)